In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a complex series of procedures used to assist with conception, offering hope to many individuals and couples struggling with infertility. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the IVF process, its indications, and what to expect during treatment.
What is IVF?
IVF is an assisted reproductive technology (ART) in which eggs are extracted from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the woman’s uterus to establish a successful pregnancy.
Why is IVF Performed?
IVF is performed to address various fertility issues, including:
- Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- Male infertility factors, such as low sperm count or motility
- Unexplained infertility
- Ovulation disorders
- Genetic disorders
- Previous unsuccessful fertility treatments
How Long is the IVF Process from Beginning to End?
The IVF process typically takes four to six weeks from the start of ovarian stimulation to the embryo transfer. However, this timeline can vary based on individual responses to treatment and the specific protocols used.
How Common is IVF?
IVF is a widely used fertility treatment. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 30,000 IVF cycles are performed annually in the United States alone, resulting in approximately 10,000 live births.
What is the Difference Between IVF and IUI (Intrauterine Insemination)?
IVF and IUI are both fertility treatments, but they differ significantly:
IVF: Involves fertilizing eggs outside the body and then transferring embryos to the uterus.
IUI: Involves placing sperm directly into the uterus during ovulation to facilitate natural fertilization.
Procedure Details:
What are the Steps of IVF Treatment?
1. Birth Control Pills or Estrogen:
Patients may begin the cycle with birth control pills or estrogen to regulate the menstrual cycle and prepare the ovaries for stimulation.
2. Ovarian Stimulation:
Medications are administered to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Monitoring through blood tests and ultrasounds ensures optimal egg development.
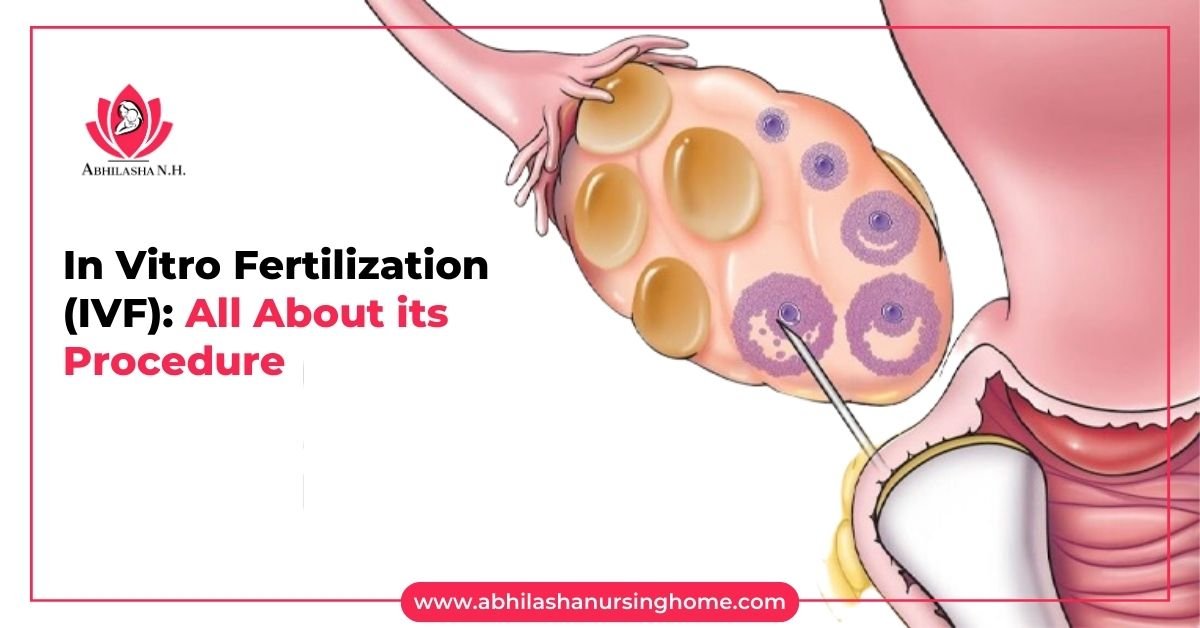
3. Egg Retrieval:
A minor surgical procedure is performed under sedation, where a needle is used to retrieve eggs from the ovaries.
4. Fertilization:
Eggs are combined with sperm in a lab. Fertilization occurs either conventionally or via intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg.
5. Embryo Development:
Fertilized eggs develop into embryos over 3-5 days. Embryos are monitored for quality before transfer.
6. Embryo Transfer:
A thin catheter transfers a selected embryo (or embryo) into the woman’s uterus. This is a simple outpatient procedure.
7. Pregnancy:
A blood test is conducted about 10-14 days after the embryo transfer to determine whether pregnancy has occurred.
Risks / Benefits:
IVF offers the benefit of enabling many people to conceive who might otherwise be unable to. However, it also carries risks, such as:
- Multiple pregnancies (if more than one embryo is transferred)
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Emotional and financial stress
When to Call the Doctor
Patients should contact their best gyno doctor if they experience severe symptoms such as:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Heavy vaginal bleeding
- Signs of infection (fever, chills)
- Complications from medication
IVF is a sophisticated and effective fertility treatment that has helped many people achieve their dream of parenthood. Understanding the procedure, its benefits, and its risks can help individuals make informed decisions and prepare for the journey ahead.